Microscope Solutions for
Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturing
Electrode Manufacturing Process
Apply the electrode material to the metal foil, which is used as a current collector. After pressing it, cut the metal foil into the size of one electrode.
Inspecting the Burrs (Projections) on the Electrode Sheet
If there are burrs (projections) on the current collector or electrodes, there is a risk of breaking through the separator and causing a short circuit, which can lead to damage, fire, or explosions. For this reason, the inspection of burrs using a microscope is required.
Our Solution
Our DSX series digital microscope can quickly and easily inspect burrs on an electrode sheet.
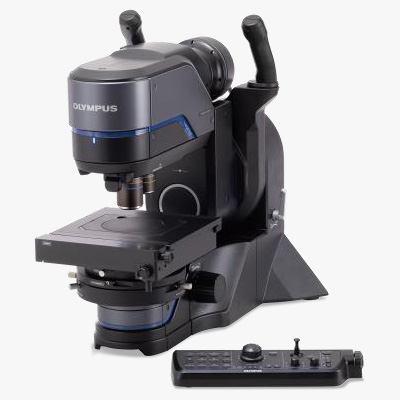 DSX series digital microscope |  Current collector and electrodes |
Inspecting the Electrode Cross Section
The power generation efficiency improves if the electrode material and the current collector are in close contact with each other. Inspectors must observe the cross section to check the placement of the materials.
Our Solution
Set the electrode vertically and observe the interface between the electrode material and current collector using our DSX series digital microscope. If the dimensions of the electrodes are large, we recommend our STM7 measuring microscope.
 DSX series digital microscope |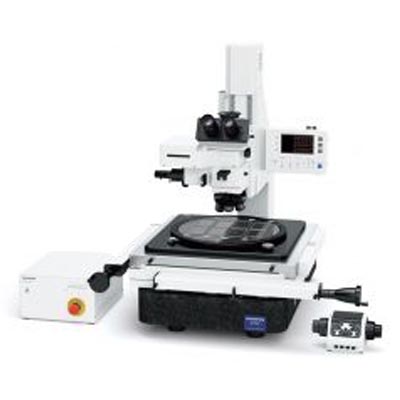  STM series measuring microscope |  Cross section of electrode |
Measuring the Surface Roughness of the Current Collector
The surface of the current collector is processed to enhance the movement of the electrodes between the collector and the active material. Inspectors must measure the collector's surface roughness to help ensure that the battery works properly.
Our Solution
Our OLS series laser scanning microscope can measure the current collector's surface roughness to make sure that the roughness f alls within a certain range. This nondestructive method can measure without making defects on the surface.
 OLS series laser scanning microscope | 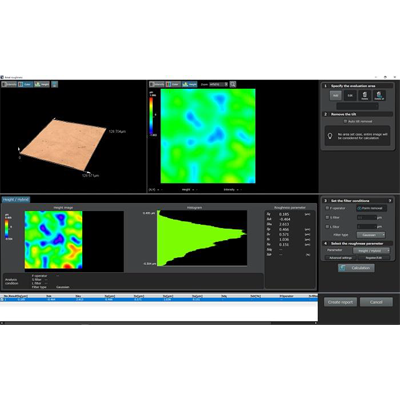 Surface roughness measurement acquired with the OLS5000 laser scanning microscope |
Application Notes
Explore related applications:
 |
|
Inspecting the Surface Roughness of the Electrode
A film called a separator is placed between the anode and cathode. Many tiny holes are opened in the separator, and the lithium ions move between the anode and cathode to generate electricity. To maintain proper adhesion with the separator, it is critical to control the surface roughness of the electrode.
Our Solution
Our With our OLS series laser scanning microscope can measure the surface roughness of the electrode. This nondestructive method can measure without making defectson the surface.
 OLS series laser scanning microscope |  Measurement of anode surface roughness |
Application Notes
Explore related applications:
 |
|
Analyzing Metal Contamination
Unexpected fires or explosions from lithium-ion batteries overheating is a major safety concern. One of the main causes of a lithium-ion battery self-igniting is an electrical short circuit due to metal contamination mixed in during the manufacturing process. Due to this risk, contamination analysis is a critical part of lithium-ion battery manufacturing.
Our Solution
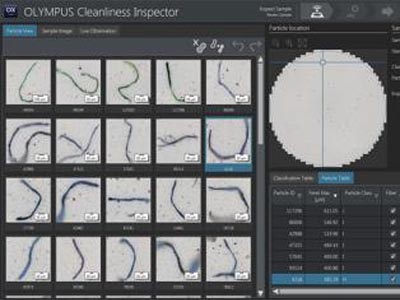
Easily analyze metal contamination using our OLYMPUS CIX100 cleanliness inspector.
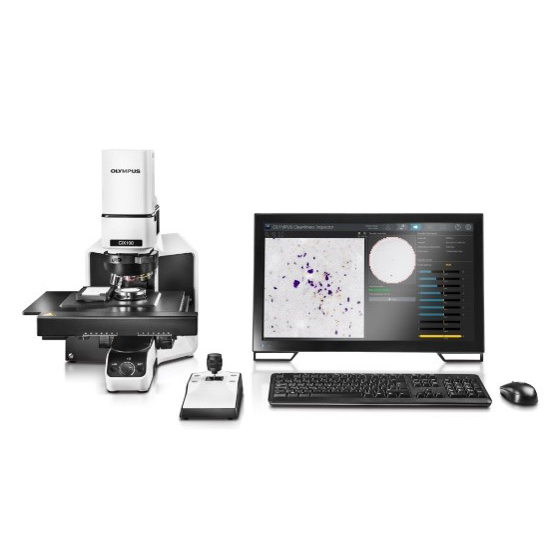 OLYMPUS CIX100 cleanliness inspector |  |
Application Notes
Explore related applications:
 |
|