Various microscopy techniques using digital microscopes
Printed Circuit Board
1. Application
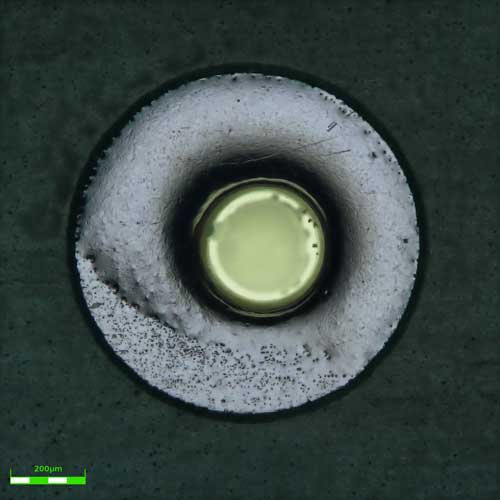
As electronic devices become smaller, through-holes on the printed circuit board (PCB) become denser. At the same time, manufacturers are placing an emphasis on the quality of the through-holes. When a through-hole is bored on the board, a smear of resin melted during the drilling process may remain. When the board is plated, the resin smear prevents conduction with the inner copper foil, resulting in a state of disconnection. Therefore, it is essential to check for the presence of resin smears before plating. Even after plating, contaminated holes may cause electric resistance to change and cause a short circuit, so it is also important to check that there is no contamination in the holes.
2. Olympus’ solution
Contaminants sticking to the inner wall of a through hole are at different heights, so vertical-direction focusing is required during observation with a microscope. With the extended focal image (EFI) function of Olympus' DSX digital microscope, the focus is shifted in the height direction while maintaining a clear view, enabling the system to automatically create a fully-focused image of the entire hole. The DSX microscope provides a variety of observation methods such as brightfield, darkfield, MIX (a combination of brightfield and darkfield), differential interference, and polarization. Users can select observation method that best suits their application with a single click, helping eliminate the complicated settings and adjustments required by conventional microscopes. The inner wall of the through-hole is dark and difficult to see in reflected illumination, but addition of transmitted illumination enables much better confirmation of the contaminants. By using both reflected and transmitted illumination, the surface of the board and the inner wall of the hole can be observed simultaneously.
Images
(1) Different microscopy techniques designed to suit your application
 Bright field |  MIX (Bright field and+ Dark field) |  Polarization |
(2) Observing a resin smear using transmitted illumination


