The Background and Problems in Engine Block Inspections
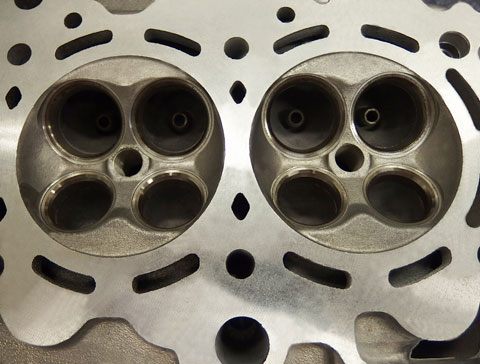
Engine blocks are the basis of automobiles. Their complicated designs and robust construction withstand fuel combustion. Virtually all components are made by sand casting. The following problems may occur with these molded components.
- Some of the melted sand becomes embedded into the final casting, and the components cannot be cleanly extracted from the molds.
- Cavities are caused by air infiltrator during casting.
- Sand cannot be cleanly extracted from highly-detailed components, causing clogs.
- Cracks and sink marks are generated in the materials that are melted at high temperatures when they cool and solidify.
- Burrs are generated after sand molding, fall into, and remain inside components.
These problems cannot be viewed directly and tend to get overlooked in visual inspections because they occur deep inside of the components. Industrial videoscopes are necessary to conduct internal inspections.
![[Remnants of sand detected by videoscope inspection]](https://industrial.evidentscientific.com.cn/data/Image/appnotes/RVI_Automotive/automobile_engine-sand_detected.jpg?rev=6F07)
[Remnants of sand detected by videoscope inspection]
Videoscope inspections are conducted in water jackets, which cool the engine. Water jackets have narrow inlets and widen up in the interior. Only videoscopes can efficiently and accurately inspect water jackets.
Benefits specific to Olympus
The most popular Olympus videoscopes used in water jacket inspections are 2 meters in length and have diameters from 2.4 mm to 5.0 mm. They are flexible and can efficiently and steadfastly conduct inspections in molding plants.
![[Insertion of thin videoscope into a water jacket]](https://industrial.evidentscientific.com.cn/data/Image/appnotes/RVI_Automotive/automobile_engine-inspection.jpg?rev=6F07)
[Insertion of thin videoscope into a water jacket]
Olympus videoscopes are adapted by automobile and automobile component manufacturers throughout the world and are typically suitable for conducting water jacket inspections:
- Dust-proof and drip-proof performance: compatible for environments, such as dusty molding plants and machining areas where cutting oil is used.
- Various types of replacement lenses: with the flexible types, replacement lenses can be selected to match the inspection applications; these lenses performances allow faster and more efficient identification of inspection locations.
- Tip articulation control that can efficiently observe the area where it is aimed: with the flexible types, the lens orientation can be suitably and swiftly operated with the controller at hand.
- Highly durable scope insertion components: the flexible types use tungsten braids, and the rigid types use SUS materials; these materials can withstand the cumbersome inspection insertions whereas the videoscopes are pushed in and pulled out repeatedly.
|
|
|
[The abrasion-resistant and durable videoscope IPLEX TX has an outer diameter that is a scant 2.4 mm, and is equipped with tip articulation control]
![[The abrasion-resistant and durable videoscope IPLEX TX has an outer diameter that is a scant 2.4 mm, and is equipped with tip articulation control]](https://industrial.evidentscientific.com.cn/data/Image/appnotes/RVI_Automotive/automobile_engine-iplex_diameter.jpg?rev=6F07)
![[The abrasion-resistant and durable videoscope IPLEX TX has an outer diameter that is a scant 2.4 mm, and is equipped with tip articulation control]](https://industrial.evidentscientific.com.cn/data/Image/appnotes/RVI_Automotive/automobile_engine-iplex_movability.jpg?rev=6F07)
![[The abrasion-resistant and durable videoscope IPLEX TX has an outer diameter that is a scant 2.4 mm, and is equipped with tip articulation control]](https://industrial.evidentscientific.com.cn/data/Image/appnotes/RVI_Automotive/automobile_engine-iplex_durability.jpg?rev=6F07)