Lithium-Ion Battery Image
Application
Secondary, or rechargeable, lithium-ion batteries used in hybrid and electric vehicles have been known to overheat and even ignite during operation. This fire hazard is largely attributed to metal contamination during the battery manufacturing process, which can lead to an eventual electrical short circuit. Thorough and reliable contamination analysis is therefore a critical aspect of technical cleanliness inspections performed on lithium-ion batteries for the automobile industry. However, conventional analytical methods have several limitations, including the following:
- Though methods such as gravimetric analysis can identify the total mass of detected contamination, they are incapable of measuring the size of each particulate so the true magnitude of the contamination remains unknown.
- The large number of test samples to inspect and the length of time required to perform each test means that contamination analysis can be very time consuming when using conventional microscopes.
- If a stereomicroscope is used for such analysis, the contamination detection ability is relatively low, making the data less reliable.
The Olympus solution
Contamination analysis using the OLYMPUS CIX100 technical cleanliness inspection system
Features of the product
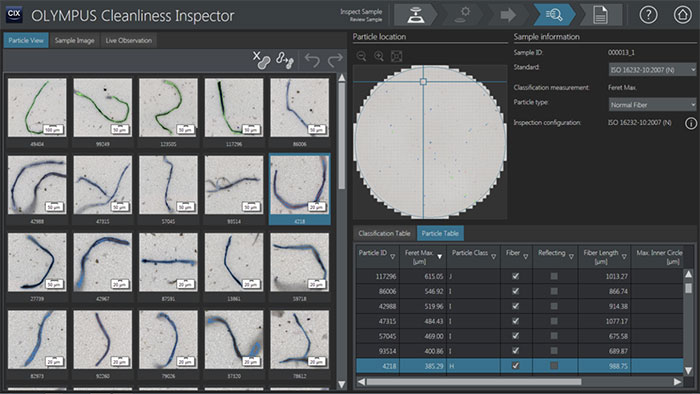
- With its high-performance industrial microscope and versatile dedicated software, the OLYMPUS CIX100 system can acquire an image of contamination in a lithium-ion battery and classify and measure the size of each contaminant particulate.
- The OLYMPUS CIX100 system’s optimized contamination analysis functionalities with easy-to-use workflows enable you to inspect test samples quickly and reliably, minimizing variation between operators.
- Olympus' high-quality industrial objectives enable the detection of microscopic contaminant particles as small as 2.5 µm (and up to 42 mm) in size.
Image
Contamination analysis image