What are Trunnions?
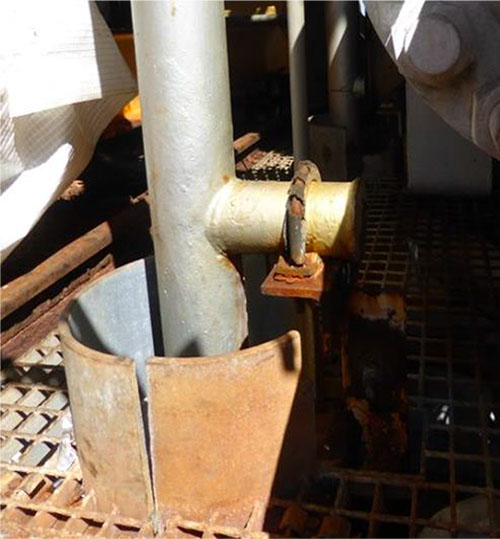

A typical trunnion above a deck penetration (Courtesy of ESR Technology)
Trunnions are a type of pipe support used extensively on most types of pipework. They are designed to support the weight of the attached spool, maintain the correct positioning of the pipework, and prevent excessive vibration and stress. They are typically welded directly on to the pipe spool.

Showing some typical trunnion configurations (Courtesy of ESR Technology)
Weep holes are normally added to the trunnions prior to welding, to allow for the escape of hot gases. These can be sealed to prevent water ingress, but most are left open. Water ingress into these spaces, especially on trunnions where any standing water is in contact with the parent spool, can create an environment of highly accelerated corrosion. The enclosed area of the pipe spool is most often uncoated, creating further corrosion issues. These corrosion issues can often go unnoticed, until the pipe spool fails and creates a loss of containment, see below;

Pipe Spool failure can create a loss of containment. (Courtesy of ESR Technology)
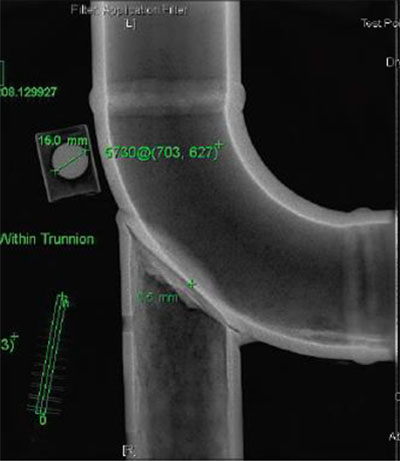
Radiograph of trunnion (Courtesy of ESR Technology)
Certain NDT techniques can be used to assess remaining wall thickness (specialist ultrasonic methods or radiography), but these can be time consuming, expensive, and come with their own limitations. The HOIS JIP states the below regarding borescopes when comparing different inspection methods for trunnions;
Methods of Inspection for Trunnions
Method | Strengths | Limitations |
Borescope video probes | Useful screening method – can confirm the absence of corrosion on external surface of process pipe inside the trunnion or possibly rank severity of any corrosion present. Allows direct visualization of the corrosion product. Rapid and simple to do. | No quantitative measure of wall loss or remaining wall thickness. Where large amounts of corrosion product are present, can be difficult to differentiate between trunnion and process pipe walls in the images. Requires weephole to be unplugged – must be refilled to prevent water ingress. Will not detect internal wall loss of process pipe – limited to external pipe surface assessment. |
As a rapid screening tool the borescope provides the simplest, fastest solution for this type of inspection. Internal visual inspections can flag issues that may need further investigation, speeding up the overall inspection workscope. Limitations include no ability to measure remaining wall thickness, and the difficulty in assessing condition where large amounts of scale are already present, see below;
Internal borescope photo showing process pipe. (Courtesy of ESR Technology)

Showing assorted pitting post-removal and surface prep of process pipework (Courtesy of ESR Technology)
Our solutions
IPLEX G-Lite systems
Our IPLEX G-Lite systems are a premier field proven system well suited for these types of inspections. The small form factor and minimal weight allow for access to restricted spaces, as well as easy manipulation and use while working at height.
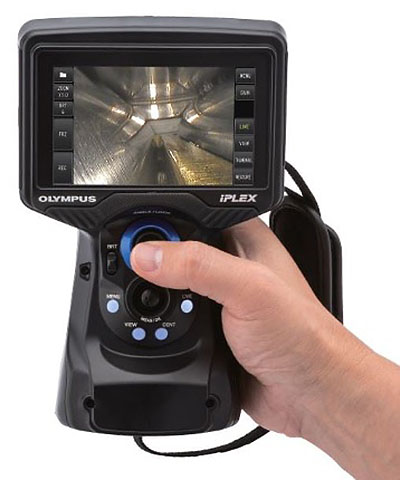

IPLEX G-Lite Videoscope
G-Lite Advantages;
- Insertion tube operable under water with standard viewing tips in cases of water ingress.
- Exceptional image quality and WIDER software helps in areas of poor visibility with corrosion present.
- Stereo measurement can allow for corrosion pit measurement where little or no external scale present.
- 3D Assist can rapidly model surface conditions in three dimensions, reducing reliance on 2D images when assessing areas of excessive corrosion or scale, while requiring only regular non-stereo lens adaptors.
- Tungsten braided insertion tube with oil-resistant coating means durability and reduced chance of breakages.
Relevant Documents & Links
HOIS Guidance on Trunnion Inspections: https://esrtechnology.com/hois/publications/publications-download/
UK HSE Safety Note regarding trunnion inspections: Corrosion in trunnion supports of pipework containing hazardous substances
Additional guidance on trunnion configurations and construction can be found as part of ASME code b31.3.