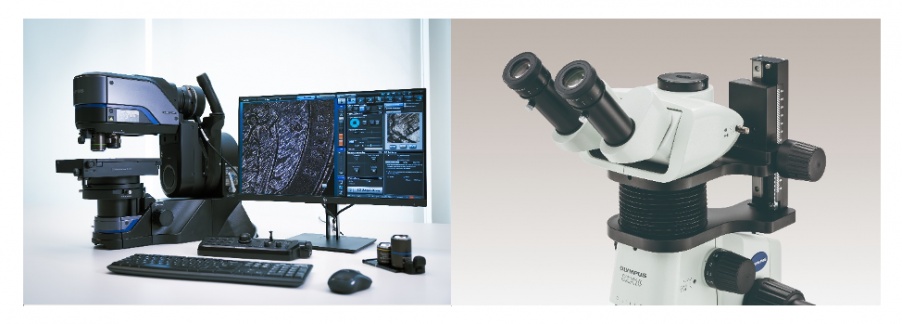
Digital and optical microscopes are essential tools in the field of microscopy. They enable scientists, researchers, inspectors, and enthusiasts to explore and analyze the microcosmic world. While both types serve the same purpose of magnifying and examining objects that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye, they differ in their mechanisms and capabilities.
In this post, we provide a detailed comparison between digital and optical microscopes, shedding light on their advantages, limitations, and ideal use cases. By understanding the differences between these two types of microscopes, you can make an informed decision when choosing the most suitable instrument for your specific needs.
Understanding Optical Microscopes
Optical microscopes, also known as light microscopes, have long been a staple in scientific research and education. They consist of a series of lenses and optical components that work together to produce an enlarged image by using light to magnify and examine specimens. They come in various configurations, including stereo microscopes, upright microscopes, and inverted microscopes.
A primary advantage of optical microscopes is their versatility provided by a broad magnification range. You can use them to observe a wide scope of samples, from cells and tissues in the life science field to solid materials in materials science and industrial labs. With high-resolution images, you can explore the fine details of samples with contrast and clarity.

The SZX10 research stereo microscope system is an example of an optical microscope
Digital Microscopes Unveiled
As a result of technological advancements in the digital imaging field, digital microscopes emerged utilizing digital cameras and image sensors to capture and display the enlarged images onto a screen or monitor. They’re also available in various forms, including handheld digital microscopes, USB microscopes, and LCD microscopes.
The ability to capture and store images digitally is one of the key benefits of the digital microscope. This enables you to document your findings, analyze them using image processing software, and conveniently share them with others. Digital microscopes also offer the flexibility of adjusting the magnification level digitally, enabling you to zoom in and out without having to change objective lenses.

The DSX1000 system is an example of a digital microscope
Digital vs. Optical Microscopes: A Comparative Analysis
So far, we have introduced digital microscopes and optical microscopes. Now let’s review their key differences and similarities:
1. Resolution and Image Quality
When it comes to resolution and image quality, optical microscopes have traditionally held an edge. High-quality lenses and optimized optical systems enable these microscopes to produce sharp and detailed images.
Yet, digital microscopes have made significant advancements in recent years with improvements in higher resolution image sensors and image processing capabilities. While they may not match the resolution of high-end optical microscopes, digital microscopes provide impressive image quality for most applications.
2. Magnification Range and Flexibility
With the availability of different objective lenses and adjustable eyepieces, optical microscopes are capable of a wide range of magnification, making them a versatile instrument for diverse samples with features of various sizes.
Digital microscopes, on the other hand, let you optically zoom in and out by simply turning the console dial. The optical zoom head covers a wide range of magnifications with a single objective. It is fully motorized, helping you to eliminate common errors that may occur when manually setting the zoom.
3. Image Capture and Documentation
The digital microscope’s ability to capture images directly assists in streamlining both examination and documentation. With integrated digital cameras, these microscopes enable you to capture still images or even record videos of your samples, which is useful for image analysis and sharing. Optical microscopes, on the other hand, typically require an external camera to capture images, adding extra steps to the process.
4. Connectivity and Data Sharing
Digital microscopes have a clear advantage when it comes to connectivity and data sharing. This enables real-time viewing, image transfer, and remote collaboration. Optical microscopes, while they can be equipped with cameras for image capture, often lack the same level of seamless connectivity.
5. Application Suitability
As technology continues to advance, the line between digital and optical microscopes becomes increasingly blurred. Some advanced digital microscopes incorporate optical components, while optical microscopes are embracing digital camera technology.
Ultimately, the choice between digital and optical microscopes depends on your specific requirements and preferences. Consider factors such as resolution, magnification range, image capture capabilities, and connectivity when making your decision. By understanding the similarities and differences between these microscope types, you can select the most suitable tool to explore the fascinating world of microscopy.
Key Takeaways about Digital and Optical Microscopes
In summary, digital and optical microscopes each have their own unique advantages and applications. Optical microscopes are versatile, offering a broad magnification range and high-resolution images, while digital microscopes provide the benefits of digital imaging, documentation, and sharing capabilities.
As technology advances, the boundaries between these two microscope types continue to blur. By considering your specific requirements and preferences, you can choose the most suitable microscope for your needs, whether it be a traditional optical microscope or a modern digital microscope. Explore the microscopic world and unlock new discoveries with the right microscope at your side!
If you’re still unsure about which microscope system is best for your application, simply reach out to our team for expert assistance.